xPression Documentum Edition
xPression Documentum Edition provides organizations the ability to quickly create well-designed, customer-facing multichannel communications with easy-to-use design tools and document templates, while providing a sophisticated layer of control over the entire document generation process. The end-to-end platform leverages existing EMC Documentum investments and provides a single platform for creating, managing, distributing, and archiving all types of customer communications to improve customer experience and speed time-to-market while substantially reducing document development and delivery costs.
taken from the xPression Documentum Edition website
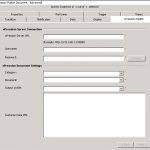
xPression Publish Document
Use the xPression Publish activity template to generate a new document from a Document Sciences xPression document template using data from the process and then map it to a package or an attachment. The variables are replaced with process data when the document is published.
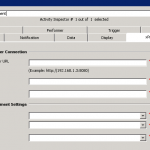
xPression Publish Document – Advanced
Use the xPression Publish Document – Advanced activity template when there are many constant values that must be mapped to process data. Instead of using the data mapper to map each variable, you can type the XML that creates the mappings for constants and adds placeholders for dynamic data. Then use the data mapper to map only the placeholder values that are created by the XML.
Question:
A health organization uses EMC Document Sciences xPression to automate business communications across the enterprise. The process needs to pass a large amnount of stati text and serveral dynamic values to the publishing function to be inserted into the document.
Which Process Builder activity template should be used to meet these requirements?
- xPression Publish Document – Mapping
- xPression Publish Document – Outbound
- xPression Publish Document – Advanced
- xPression Publish Document
Answer: xPression Publish Document – Advanced
xPression Publish Document – Mapping and xPression Publish Document – Outbound does not exists as process activity.
xPression Publish Document has no XML functionality. xPression Publish Document – Advanced is correct, because you can use the Customer Data XML property to submit several dynamic values.